Prices have fluctuated since then, but gas has continued to be plentiful and cheap. This has had two effects on coal. One is that cheap gas displaces coal in existing power systems. Secondly, cheap gas increases the incentives to finally retire old coal-fired plants from the 1940s and 1950s.
Why is use of coal declining worldwide?
What was one of the factors for the decrease in demand for coal?
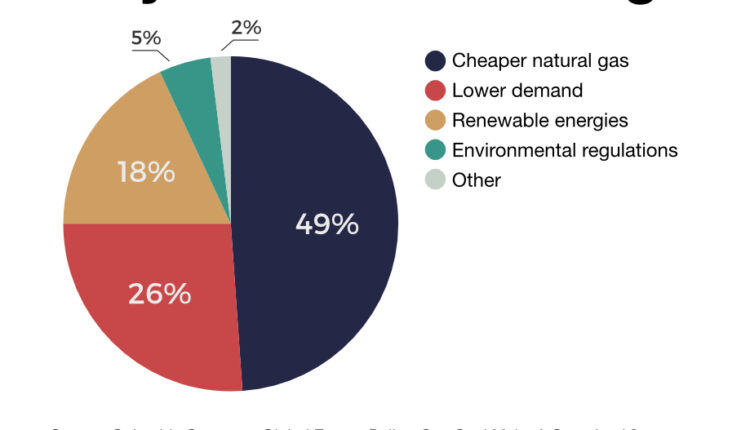
The shift away from coal was mainly driven by lower natural gas prices due to the shale revolution and stagnant U.S. electricity demand, and to a lesser extent by policy-supported growth in wind and solar generation.
Is demand for coal decreasing?
Why is coal a dying industry?
This is a result of the declining economics of coal power plants due to low natural gas prices, increasing numbers of low-cost renewable plants, and more stringent environmental regulations.
What is the biggest problem with coal?
Coal impacts: air pollution They include mercury, lead, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulates, and various other heavy metals. Health impacts can range from asthma and breathing difficulties, to brain damage, heart problems, cancer, neurological disorders, and premature death.
When did the coal industry decline?
Coal prices fell in the 1980s, partly in response to oil price decline, but primarily in response to the large increase in supply worldwide which was brought about by the earlier price surge. During this period, the industry in the U.S. moved to low-sulfur coal.
Who is responsible for coal shortage?
Why is coal being phased out of the economy?
Coal is the most carbon intensive fossil fuel and phasing it out is a key step to achieve the emissions reductions needed to limit global warming to 1.5°C, as enshrined in the Paris Agreement.
Will coal ever run out?
According to the World Coal Association, there are an estimated 1.1 trillion tonnes of coal reserves across the world. At our current rates of production and consumption, there is enough coal to last us 150 years. By around 2168, coal will be no more (unless we discover new deposits which push that date back).
Will coal make a comeback?
“Coal is definitely making a comeback, with skyrocketing natural gas prices and drought,” Ole Hvalbye, an analyst at Swedish bank SEB, told Insider.
What will replace coal in the future?
Cleaner alternatives like natural gas can also help bridge the energy transition towards a greener future. Carbon capture and storage technology may be a viable solution to ease the transition away from coal, but it is currently less cost-competitive than other low-carbon energy sources such as solar and wind.
Why is use of coal declining worldwide quizlet?
Why is use of coal declining worldwide? – Power plants using different fuels are easier and cheaper to operate.
When did the coal industry decline?
Coal prices fell in the 1980s, partly in response to oil price decline, but primarily in response to the large increase in supply worldwide which was brought about by the earlier price surge. During this period, the industry in the U.S. moved to low-sulfur coal.
Why is it difficult to replace coal?
The short answer is coal is cheap and plentiful. But even as renewables become more competitive on price, coal isn’t that easy to get rid of. Electricity needs are soaring as the world’s population and prosperity increase, and renewables simply aren’t enough to satisfy that growth in demand.
Is coal growing or shrinking?
Today, coal is still the largest source of electricity, though its share is steadily shrinking as other sources of power come online, from nuclear to wind.
How long will the coal industry last?
Who is the biggest coal supplier in the world?
China is the largest coal-producing country in the world, with production reaching 3,942 million tonnes, a 2.5% growth.
Who is the largest importer of coal?
vor 6 Tagen
How long does it take for coal to replenish?
Because coal takes millions of years to develop and there is a limited amount of it, it is a nonrenewable resource. The conditions that would eventually create coal began to develop about 300 million years ago, during the Carboniferous period.
Is the earth still making oil?
By 1906, that number was 126 million barrels per year. Today, the U.S. produces about 6.8 billion barrels of oil every year. According to OPEC, more than 70 million barrels are produced worldwide every day. That is almost 49,000 barrels per minute.
How many more years of coal is left?
Coal Reserves in the United States The United States has proven reserves equivalent to 347.7 times its annual consumption. This means it has about 348 years of Coal left (at current consumption levels and excluding unproven reserves).