It will affect global transportation and international trade Our major transportation systems, including trucking, rail and sea transportation of goods, depend greatly on fossil fuels. Without diesel and bunker fuel, large-scale international trade would have no choice but to shut down.
What will happen if there is no coal left on Earth?
Explanation: If coal and petroleum will get exhausted it will be very difficult for us to transport because most vehicles depends on petroleum, Transport on Earth will became complicated, and if coal will get exhausted we will lose an unique fossil fuel. Coal is used in various domestic and industrial purposes.
Can we run out of coal?
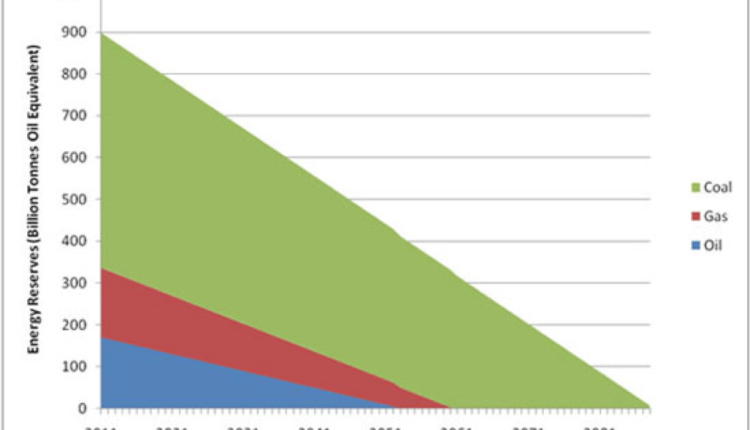
According to the World Coal Association, there are an estimated 1.1 trillion tonnes of coal reserves across the world. At our current rates of production and consumption, there is enough coal to last us 150 years. By around 2168, coal will be no more (unless we discover new deposits which push that date back).
How many years do we have until coal runs out?
Conclusion: how long will fossil fuels last? It is predicted that we will run out of fossil fuels in this century. Oil can last up to 50 years, natural gas up to 53 years, and coal up to 114 years. Yet, renewable energy is not popular enough, so emptying our reserves can speed up.
Can the world do without coal?
Recent successes in developing shale gas and oil have led some campaigners to imply the world could do without coal. But the effort to put coal off limits is doomed to fail. Coal resources will remain an essential part of the energy mix far into the future.
Is the earth still making oil?
By 1906, that number was 126 million barrels per year. Today, the U.S. produces about 6.8 billion barrels of oil every year. According to OPEC, more than 70 million barrels are produced worldwide every day. That is almost 49,000 barrels per minute.
Is there anything that can replace coal?
Does coal grow back?
Since coal comes from plants, and plants get their energy from the sun, the energy in coal also came from the sun. The coal we use today took millions of years to form. We can’t make more in a short time. That is why coal is called nonrenewable.
What will replace coal in the future?
Cleaner alternatives like natural gas can also help bridge the energy transition towards a greener future. Carbon capture and storage technology may be a viable solution to ease the transition away from coal, but it is currently less cost-competitive than other low-carbon energy sources such as solar and wind.
Why is the US not producing oil?
The reason that U.S. oil companies haven’t increased production is simple: They decided to use their billions in profits to pay dividends to their CEOs and wealthy shareholders and simply haven’t chosen to invest in new oil production.
How much fuel is left in the world?
The world has proven reserves equivalent to 52.3 times its annual consumption. This means it has about 52 years of gas left (at current consumption levels and excluding unproven reserves).
Why is coal so important?
Coal is primarily used as fuel to generate electric power in the United States. In coal-fired power plants, bituminous coal, subbituminous coal, or lignite is burned. The heat produced by the combustion of the coal is used to convert water into high-pressure steam, which drives a turbine, which produces electricity.
Why will we run out of coal?
Coal is not a renewable resource. It will run out in a little more than 100 years, if we burn it all and move it from the ground to our atmosphere.
Why there is no future for coal?
Flat electricity demand compounds the challenge for coal. A recovery in domestic coal demand is not likely. Inexpensive natural gas and renewable power are not going away. New coal-fired generation capacity is much more expensive to build and more difficult to site and permit than natural gas or renewable facilities.
Is the earth still making coal?
The process of coal formation is still taking place today, says Bailey. “The precursor to coal is called peat, and that is just uncompressed plant matter.” Peat accumulates in wet swampy environments known as mires, and that process is taking place today in areas such as Indonesia and even the Antiplano in the Andes.
Why can’t we quit oil?
We haven’t found a good substitute for oil, in terms of its availability and fitness for purpose. Although the supply is finite, oil is plentiful and the technology to extract it continues to improve, making it ever-more economic to produce and use. The same is also largely true for natural gas.
Which country does not use coal?
Belgium, Austria and Sweden are the other three European countries to have already stopped using coal for power generation. Although a hefty 60 to 70 per cent of its electricity comes from renewable sources, Portugal still relies heavily on imported fossil fuels to meet overall energy needs.
Can the world exist without oil?
Energy. A sudden loss of oil supplies would make it impossible to meet world energy needs. Countries have very varying stocks of natural gas which they could tap, and Johansen says such resources would be quickly depleted.
Do we only have 40 years of oil left?
World Oil Reserves The world has proven reserves equivalent to 46.6 times its annual consumption levels. This means it has about 47 years of oil left (at current consumption levels and excluding unproven reserves).
Can you make electricity without coal?
Electricity can be produced from a variety of energy sources, including natural gas, coal, nuclear energy, wind energy, hydropower, as well as solar energy and stored as hydrogen or in batteries.
Can nuclear power replace coal?
The case study found that greenhouse gas emissions in a region could fall by 86% when nuclear power plants replace large coal plants, which is equivalent to taking more than 500,000 gasoline-powered passenger vehicles off the roads. It could also increase employment and economic activity within those communities.
Can nuclear energy replace coal?
NuScale VOYGR™ plants are the ideal solution to replace and make the best use of retiring coal and other fossil fuel plants. They provide a clean and economical option. Nuclear provides carbon-free energy and is cost competitive, with more long-term price predictability than natural gas.