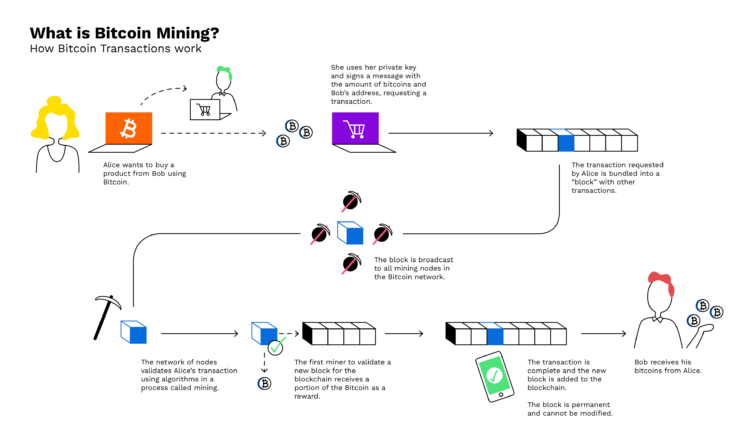
Why Do Bitcoins Need to Be Mined? Because they are entirely digital records, there is a risk of copying, counterfeiting, or double-spending the same coin more than once. Mining solves these problems by making it extremely expensive and resource-intensive to try to do one of these things or otherwise “hack” the network.
Why do Cryptocurrencies need miners?
Bitcoin runs on a decentralized computer network or distributed ledger that tracks transactions in the cryptocurrency. When computers on the network verify and process transactions, new bitcoins are created, or mined. These networked computers, or miners, process the transaction in exchange for a payment in Bitcoin.
Does every crypto have to be mined?
However, there are a lot of cryptocurrencies that do not support mining. Many of these are “proof-of-stake” cryptocurrencies, which rely on a more energy-efficient process known as staking. This involves putting some crypto at risk in order to submit a new block and earn a reward.
Why do Cryptocurrencies need miners?
Bitcoin runs on a decentralized computer network or distributed ledger that tracks transactions in the cryptocurrency. When computers on the network verify and process transactions, new bitcoins are created, or mined. These networked computers, or miners, process the transaction in exchange for a payment in Bitcoin.
How long it will take to mine 1 Bitcoin?
How Long Does It Take to Mine One Bitcoin? In general, it takes about 10 minutes to mine a block, and a block will award a number of coins to whoever mines it. Unfortunately because of the sheer number of people mining coins solo miners are a rarity because the odds of being the one to discover a block are very low.
Can cryptocurrency work without miners?
Unlike the Bitcoin blockchain network, private blockchains generally operate without miners through the help of nodes. They are also more energy-efficient at adding blocks. Unlike public blockchains, private blockchains are accessible only to verified participants. In addition, private networks may be hidden.
What happens when no more Bitcoin to mine?
What Happens to Mining Fees When Bitcoin’s Supply Limit Is Reached? Bitcoin mining fees will disappear when the Bitcoin supply reaches 21 million. Miners will likely earn income only from transaction processing fees, rather than a combination of block rewards and transaction fees.
Which crypto Cannot be mined?
Some non-minable coins are for example XRP, EOS, Stellar and NEM. These are cryptocurrency Projects where a developer has completely premined the coins at the start of the project and then later distributed them to the public. So in this scenario all the coins are premined upfront and are usually sold in ICO.
What happens to Crypto when all coins are mined?
When all bitcoin have been mined, miner revenue will depend entirely on transaction fees. The price and purchasing power of bitcoin will adjust to the lack of new supply. The scarcity of Bitcoin will make it more attractive to investors and users.
Why do Cryptocurrencies need miners?
Bitcoin runs on a decentralized computer network or distributed ledger that tracks transactions in the cryptocurrency. When computers on the network verify and process transactions, new bitcoins are created, or mined. These networked computers, or miners, process the transaction in exchange for a payment in Bitcoin.
Who is the real inventor of Bitcoin?
Key Takeaways. Satoshi Nakamoto is the pseudonym used by the creator or creators of Bitcoin. The identity of Satoshi Nakamoto is not publicly known. One of the first major public investigations ended with Dorian Nakamoto being identify as Bitcoin’s creator, but he continues to decline the claim.
How many ethereum are left?
Why is Bitcoin 21 million limit?
Since Bitcoins are intended for transactional use, just like paper currency, too many Bitcoins in the market could generate wild price swings. With that in mind, the inventor stipulated a 21 million Bitcoin limit to control the supply and, thus, future price fluctuations.
What happens when crypto reaches max supply?
What Happens When Circulating Supply Reaches Max Supply? If the circulating supply and the max supply are equal, this means all coins were released in circulation. The crypto price could go up or down depending on market conditions, but nothing drastic will happen.
Which crypto is mined fastest?
Answer: Monero is the easiest cryptocurrency to mine now because it can be mined via browser extensions and free software over websites. It is even mined via crypto jacking. The mining code can also easily be incorporated into apps and websites to facilitate mining.
Is crypto real money?
Cryptocurrency (or “crypto”) is a class of digital assets created using cryptographic techniques that enable people to buy, sell or trade them securely. Unlike traditional fiat currencies controlled by national governments, cryptocurrencies can circulate without a monetary authority such as a central bank.
What would happen if crypto mining stopped?
What happens to bitcoin if everyone stops mining? If nobody mined the difficulty would drop severely so that anybody could mine with a PC or graphics card again (like the good old days). If you mean cometely then the network would grind to a halt and transactions wouldn’t process.
Could Bitcoin disappear?
Can you mine 1 Bitcoin a day?
To put it another way, you would need to use specialized hardware called ASICs (such as Antminer S19 Pro), with a hash power between 95 and 110.0 TH/s. These devices can cost up to $17k. With 5–10 ASIC miners, you can mine 0.01 BTC per day. But to get one BTC, it would take about 100 days of mining.
How much Bitcoin can I mine in a day?
How many Bitcoin can you mine a day? Based the mining hardware inputs provided, 0.00047881 Bitcoin can be mined per day with a Bitcoin mining hashrate of 140.00 TH/s, a block reward of 6.25 BTC, and a Bitcoin difficulty of 36,762,198,818,467.00.
What happens if you mine 1 Bitcoin?
So there’s not a way to mine just 1 Bitcoin. You either win the block reward and receive 6.25 Bitcoin or you get nothing.
Why do Cryptocurrencies need miners?
Bitcoin runs on a decentralized computer network or distributed ledger that tracks transactions in the cryptocurrency. When computers on the network verify and process transactions, new bitcoins are created, or mined. These networked computers, or miners, process the transaction in exchange for a payment in Bitcoin.