The Bitcoin network is secured by mining, a process that validates transactions on the network and mints new bitcoin at the same time.
What is the role of a miner on the Bitcoin network?
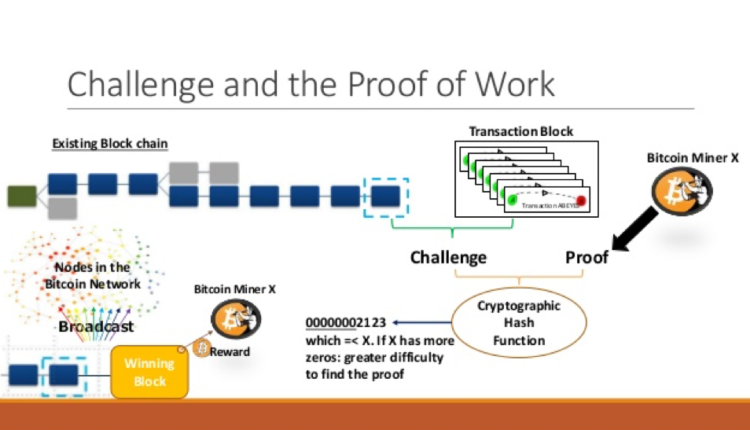
Bitcoin mining is done to record current bitcoin transactions in blocks, which are then added to a blockchain, or the record of past transactions. Bitcoin miners use software to solve transaction-related algorithms that check bitcoin transactions. In return, miners are awarded a certain number of bitcoin per block.
Do miners control the blockchain?
Since miners process transactions, it would be straightforward to assume that they can decide which transactions make it into the blockchain or not, and act as new middlemen. In practice, it is difficult for miners to set or change any rules, or to prevent transactions from being added to the blockchain.
Is mining Bitcoin secure?
The risks of mining are often financial and regulatory. As aforementioned, Bitcoin mining, and mining in general, is a financial risk because one could go through all the effort of purchasing hundreds or thousands of dollars worth of mining equipment only to have no return on their investment.
Do miners control the blockchain?
Since miners process transactions, it would be straightforward to assume that they can decide which transactions make it into the blockchain or not, and act as new middlemen. In practice, it is difficult for miners to set or change any rules, or to prevent transactions from being added to the blockchain.
How long it will take to mine 1 Bitcoin?
It takes around 10 minutes to mine just one Bitcoin, though this is with ideal hardware and software, which isn’t always affordable and only a few users can boast the luxury of. More commonly and reasonably, most users can mine a Bitcoin in 30 days.
Does a Bitcoin miner need to be connected to the Internet?
Delivering bitcoin transaction data to miners requires internet-enabled devices. As a digital currency, you cannot buy, sell or exchange bitcoin without the internet. As such, even a single day without internet access could cost bitcoin miners, exchanges, and traders millions.vor 2 Tagen
Who controls the Bitcoin network?
Nobody owns the Bitcoin network much like no one owns the technology behind email. Bitcoin is controlled by all Bitcoin users around the world. While developers are improving the software, they can’t force a change in the Bitcoin protocol because all users are free to choose what software and version they use.
Who controls most of bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin is a system of rules without rulers. There’s no president or CEO, no oversight board or ruling council. No one person or group can unilaterally make changes to the software that runs the network. Therefore, no one can be said to be in control.
What happens to miners when all Bitcoin is mined?
Can Bitcoin mining be traced?
Because the Bitcoin blockchain is a public ledger, all payments flowing between addresses are observable. However, some Bitcoin users adopt strategies to impede tracing by moving their funds over long chains of multiple addresses and splitting payments.
Why is mining crypto illegal?
The legality of Bitcoin mining is entirely dependent on your geographical location. The concept of Bitcoin has the potential to undermine fiat currency dominance and government control over financial markets. As a result, Bitcoin is completely illegal in some jurisdictions.
What is the function of a miner?
A miner is a person who extracts ore, coal, chalk, clay, or other minerals from the earth through mining. There are two senses in which the term is used. In its narrowest sense, a miner is someone who works at the rock face; cutting, blasting, or otherwise working and removing the rock.
What is the role of a miner?
Underground production and development miners drill, blast, operate mining machinery and perform related duties to extract coal and ore in underground mines and construct mine tunnels, passageways and shafts to facilitate mining operations.
What is the purpose of a miner?
Miners operate machinery and equipment to dig, load and transport ore, coal, rock and sand underground or in open-cut mines. It’s common for Miners to work in rural and remote locations, often living a fly-in/fly-out lifestyle.
How does a bitcoin miner get paid?
Bitcoin miners earn rewards, paid in bitcoin, for verifying a new block of bitcoin transactions. Miners who successfully validate a block earn a reward of 6.25 bitcoins, which, depending on its market value, could be a lot.
Do miners control the blockchain?
Since miners process transactions, it would be straightforward to assume that they can decide which transactions make it into the blockchain or not, and act as new middlemen. In practice, it is difficult for miners to set or change any rules, or to prevent transactions from being added to the blockchain.
Is mining Bitcoin secure?
The risks of mining are often financial and regulatory. As aforementioned, Bitcoin mining, and mining in general, is a financial risk because one could go through all the effort of purchasing hundreds or thousands of dollars worth of mining equipment only to have no return on their investment.
How much RAM do you need to mine Bitcoin?
RAM — Higher RAM does not mean that you get a better mining performance, so we recommend using anywhere between 4GB and 16GB of RAM. When deciding what size RAM best suits your needs, look at the operating system for mining and whether or not virtual memory is used.
Will Bitcoin mining damage my computer?
Is cryptocurrency mining bad for your graphics card? The answer isn’t so simple. Mining harms your GPU in the sense that one of its by-products is producing excess heat. If you run your mining setup 24/7 at a high temperature – above 80 oC or 90 oC – the GPU could sustain damage that will severely affect its lifespan.
Can you mine Bitcoins with a normal computer?
Can the Bitcoin network be hacked?
Each token is assigned a private key, which is held by the owner or custodian appointed by the owner. The token and number itself could be hacked, but it would take years of attempts to be successful because of the encryption methods.