One is that cheap gas displaces coal in existing power systems. Secondly, cheap gas increases the incentives to finally retire old coal-fired plants from the 1940s and 1950s. Figure 5 shows the expansion of natural gas in electricity generation, in parallel with the decline of coal.
What factors caused the decline in coal production and price?
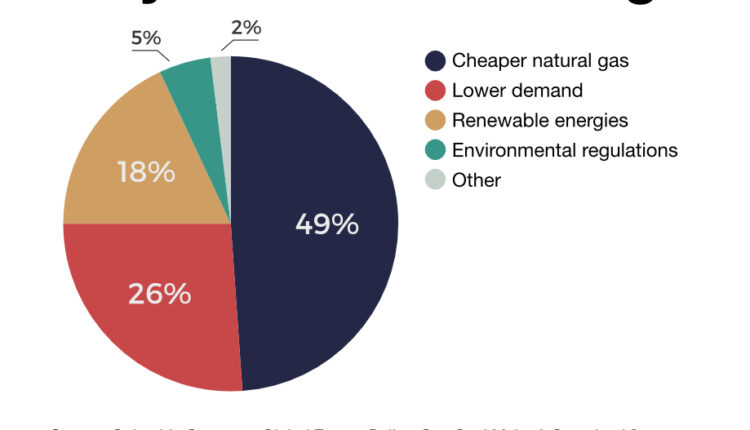
The shift away from coal was mainly driven by lower natural gas prices due to the shale revolution and stagnant U.S. electricity demand, and to a lesser extent by policy-supported growth in wind and solar generation.
Why is use of coal declining worldwide?
When did coal stop being used?
Is demand for coal decreasing?
What is the biggest problem with coal?
Coal impacts: air pollution They include mercury, lead, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulates, and various other heavy metals. Health impacts can range from asthma and breathing difficulties, to brain damage, heart problems, cancer, neurological disorders, and premature death.
Why is the coal industry likely to decline in the future?
Flat electricity demand compounds the challenge for coal. A recovery in domestic coal demand is not likely. Inexpensive natural gas and renewable power are not going away. New coal-fired generation capacity is much more expensive to build and more difficult to site and permit than natural gas or renewable facilities.
Are we running out of coal?
What will replace coal in the future?
Cleaner alternatives like natural gas can also help bridge the energy transition towards a greener future. Carbon capture and storage technology may be a viable solution to ease the transition away from coal, but it is currently less cost-competitive than other low-carbon energy sources such as solar and wind.
Why is there sudden coal shortage?
The sudden surge in demand can be attributed to the country’s industries as they pick up operations after the second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. And despite having the fourth-largest reserves in the world, the domestic producers of coal are unable to meet the demands.
Is the use of coal increasing or decreasing?
Is coal growing or shrinking?
Today, coal is still the largest source of electricity, though its share is steadily shrinking as other sources of power come online, from nuclear to wind.
What are two problems with coal?
Emissions from burning coal Sulfur dioxide (SO2), which contributes to acid rain and respiratory illnesses. Nitrogen oxides (NOx), which contribute to smog and respiratory illnesses. Particulates, which contribute to smog, haze, and respiratory illnesses and lung disease.
What are the main problems with coal mining?
There are significant environmental impacts associated with coal mining and use. It could require the removal of massive amounts of top soil, leading to erosion, loss of habitat and pollution. Coal mining causes acid mine drainage, which causes heavy metals to dissolve and seep into ground and surface water.
What happens if coal runs out?
Our major transportation systems, including trucking, rail and sea transportation of goods, depend greatly on fossil fuels. Without diesel and bunker fuel, large-scale international trade would have no choice but to shut down.
Will coal make a comeback?
“Coal is definitely making a comeback, with skyrocketing natural gas prices and drought,” Ole Hvalbye, an analyst at Swedish bank SEB, told Insider.
Will coal run out in 50 years?
It is predicted that we will run out of fossil fuels in this century. Oil can last up to 50 years, natural gas up to 53 years, and coal up to 114 years. Yet, renewable energy is not popular enough, so emptying our reserves can speed up.
What energy can replace coal?
In all regions and for all siting limits, retiring coal plants are replaced with a mix of wind and solar power. Operations and maintenance jobs account for 57% to 92% of the replacement employment at wind and solar facilities while construction jobs play a lesser role, according to the study.
Can you make electricity without coal?
Electricity can be produced from a variety of energy sources, including natural gas, coal, nuclear energy, wind energy, hydropower, as well as solar energy and stored as hydrogen or in batteries.
Who is responsible for coal shortage?
Why is use of coal declining worldwide quizlet?
Why is use of coal declining worldwide? – Power plants using different fuels are easier and cheaper to operate.